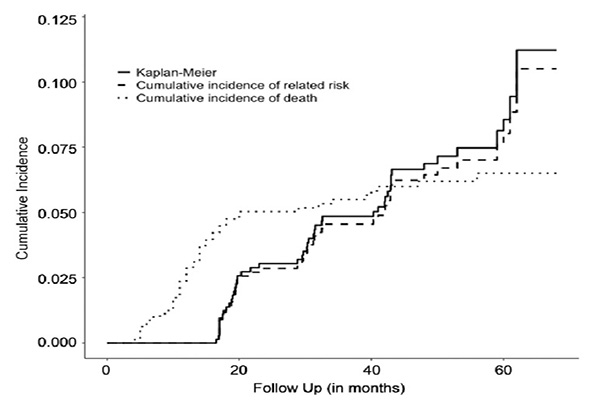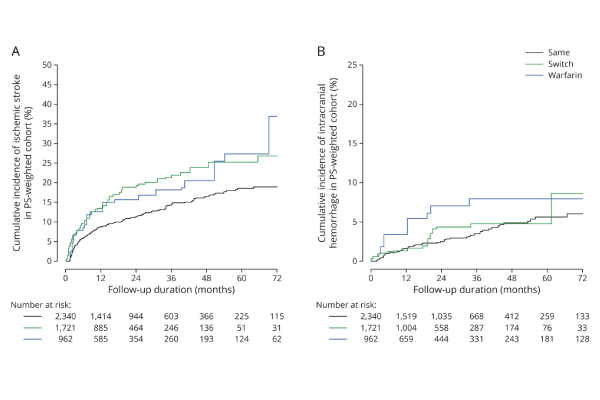
Optimal antithrombotic strategy for preventing stroke in AF patients
In Hong Kong, atrial fibrillation (AF)-related stroke constitutes almost 30% of all ischemic stroke cases. Although oral anticoagulation effectively reduces ischemic stroke risk by 60-70% in AF patients, a significant proportion of them may still suffer from ischemic stroke despite DOACs. CUHK Neurology conducted the world’s first population-based study to evaluate the impact of different antithrombotic approaches on patient outcomes after the first episode of ischemic stroke despite taking direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). It revealed an elevated risk of recurrent ischemic stroke in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients on alternative oral anticoagulants.Summary
Full Article